frameless torque motor. But what exactly is a frameless torque motor, and why is it becoming the superior choice for high-performance applications? This guide will explain everything you need to know.
What is a Frameless Torque Motor?
A frameless torque motor, also known as a direct drive motor (DD motor), is a specialized type of permanent magnet motor that is delivered without a frame, housing, bearings, or a shaft. It consists of just two core components: a stator and a rotor. This unique, unhoused design is its greatest strength.
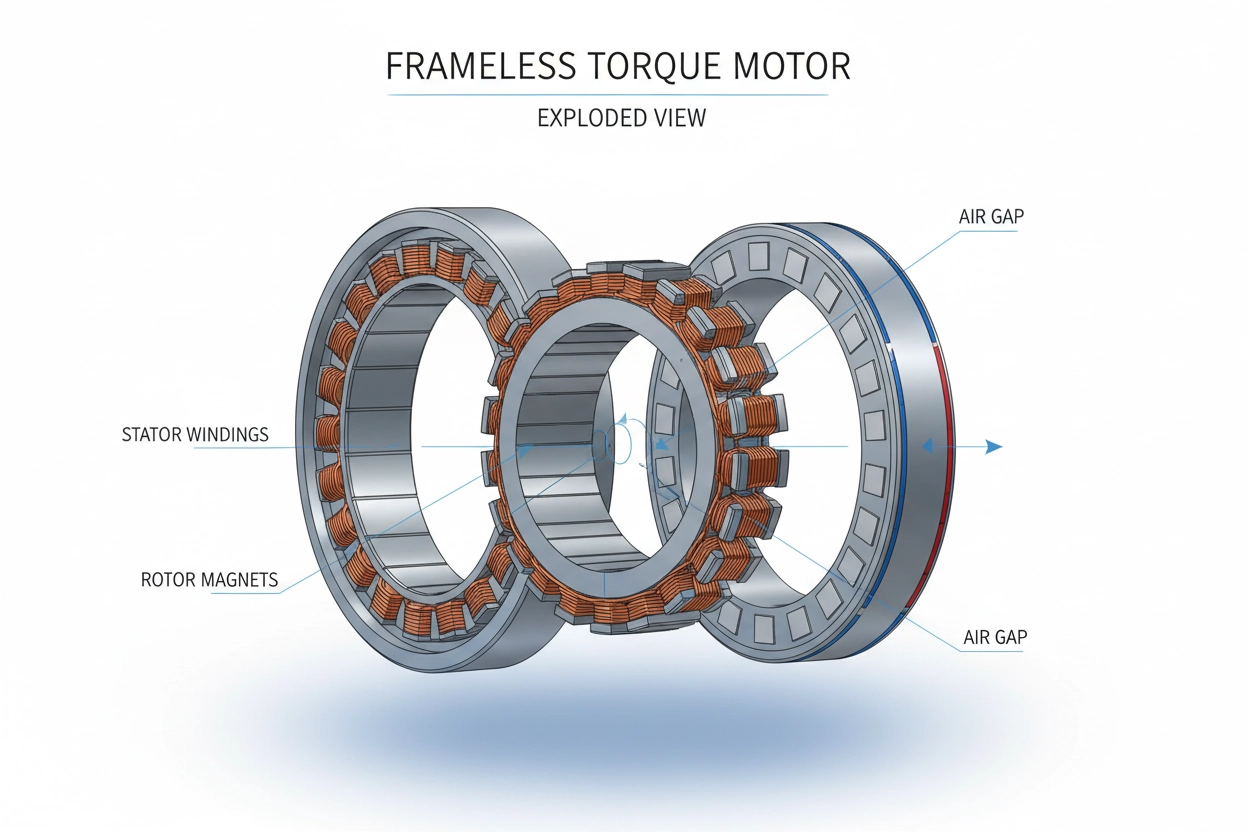
The Core Components: Stator and Rotor
The stator is the stationary outer ring containing meticulously wound copper coils. The rotor is the rotating inner ring fitted with powerful permanent magnets. Because they are separate components, engineers can integrate them directly into the machine’s structure, using the machine’s own bearings and shaft to support the rotor.
Understanding the Direct Drive (DD Motor) Principle
The name “direct drive” comes from the fact that the load is directly coupled to the motor’s rotor. This eliminates the need for mechanical transmission elements like gearboxes, belts, or pulleys. The motor directly drives the load, resulting in a mechanically simpler and more efficient system.
How Direct Drive Integration Simplifies Machine Design
By integrating the motor components directly into the mechanics, engineers can create exceptionally compact and lightweight systems. This simplified design reduces the overall part count, minimizes potential points of failure, and often leads to a smaller machine footprint.
Key Advantages of a Direct Drive Motor
The decision to use a direct drive motor provides several transformative benefits for machine performance and design. These advantages are the primary reason for their adoption in demanding industries.
Unmatched High Torque Density
High torque density is arguably the most significant advantage. Frameless motors are designed with a large diameter and a short axial length, a geometry that is optimized for producing the maximum amount of torque for their size and weight. This allows for powerful acceleration in a very small package.
Achieving Zero Backlash and Superior Rigidity
Because there are no gears, belts, or other transmission components, direct drive systems have absolutely zero backlash. This complete absence of “play” in the system, combined with a very stiff mechanical connection, results in superior positional accuracy and faster settling times.
The Benefit of a Compact, Low-Profile Design
The frameless nature allows the motor to become an integral part of the machine structure rather than a bulky attachment. This leads to a significantly more compact, low-profile design, which is critical for applications like robotic joints and gimbals where space is at a premium.
Increased Efficiency and Long-Term Reliability
Fewer moving parts means fewer sources of friction and wear. Direct drive systems are highly efficient because motor power is not lost through a gearbox. This also leads to greater reliability and a longer operational lifespan with virtually no maintenance.
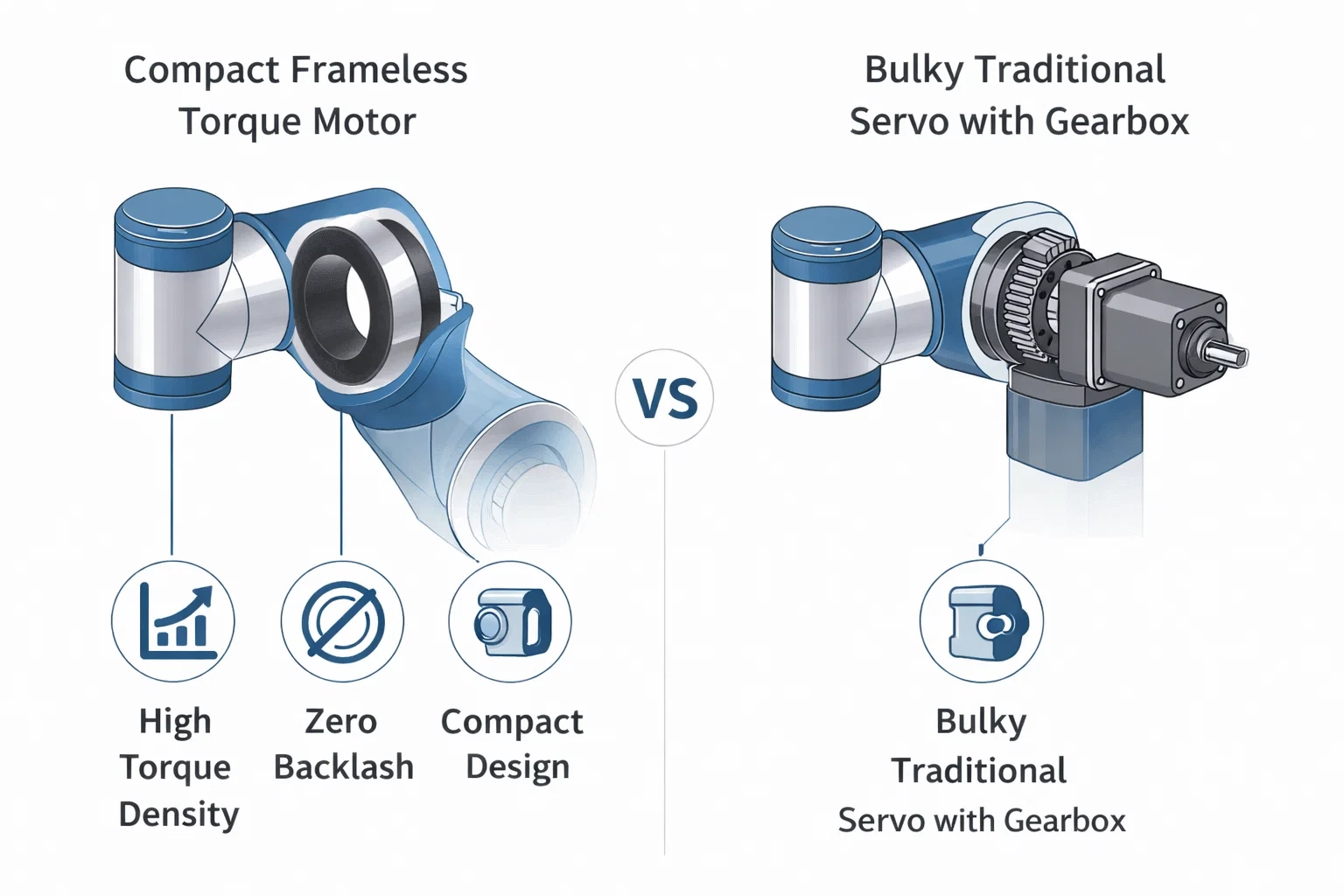
Frameless vs. Traditional Servo Motors: A Comparison
How does a frameless motor stack up against a conventional, housed servo motor? The differences are fundamental.
Mechanical Complexity and Parts Count
A traditional system requires a servo motor, a coupling, a gearbox, and the necessary mounting hardware. A frameless system eliminates all these extra components, drastically reducing mechanical complexity and simplifying the assembly process.
Differences in Performance, Accuracy, and Response
The direct coupling in a frameless system provides a much faster and more accurate response. There is no transmission elasticity or backlash to overcome, so the system can execute commands with higher fidelity and settle into position more quickly.
A Look at Size, Weight, and Power (SWaP)
For any application where Size, Weight, and Power (SWaP) are critical metrics, frameless motors are the clear winner. They offer a much better torque-to-weight ratio and allow for designs that would be impossible with traditional motors.
Common Applications for High Torque Density Motors
The unique benefits of frameless motors make them the ideal choice for a wide range of advanced applications.
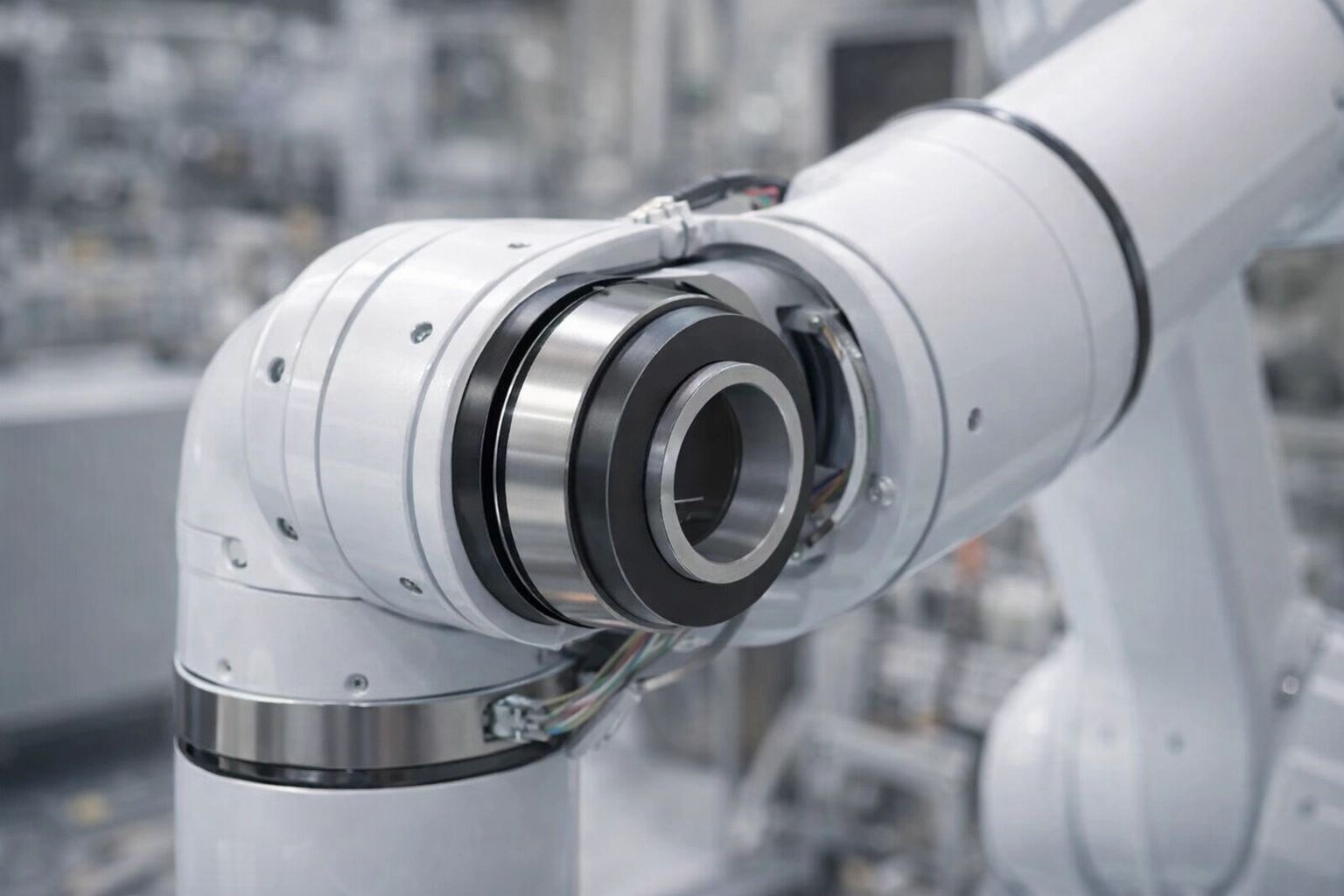

A frameless torque motor integrated seamlessly inside a modern robotic arm joint, showcasing a common application.
Robotic Joints and Automation Systems
The compact size and high torque of frameless motors are perfect for the joints of industrial and collaborative robots, where space is minimal and dynamic performance is paramount.
Precision Spindles in CNC Machine Tools
In high-speed CNC machining, direct drive spindles powered by frameless motors provide the smooth, vibration-free rotation needed for superior surface finishes.
Gimbals for Defense and Medical Imaging
For camera gimbals, satellite tracking, and medical imaging equipment (like MRI or CT scanners), the smooth motion and precise pointing accuracy of frameless motors are essential. To see how this technology is implemented, you can .
Conclusion: Is a Frameless Torque Motor Right for Your Project?
If your application demands high torque, exceptional precision, a compact form factor, and a simplified mechanical design, a frameless torque motor is almost certainly the right choice. By eliminating gearboxes and directly driving the load, you unlock a new level of performance and design freedom.
Evaluate your project’s needs against the key benefits of high torque density, zero backlash, and integration simplicity. If these align with your goals, embracing could be the most impactful design decision you make.
FAQ Section: Your Frameless Motor Questions Answered
Q1: What’s the difference between an inrunner and outrunner frameless torque motor? In an “inrunner” design (the most common type), the rotor rotates inside the stationary stator. In an “outrunner,” the stator sits in the middle and the rotor (shaped like a bell) rotates around it. The choice depends on the specific mechanical integration requirements.
Q2: Do frameless motors require a separate encoder and bearings? Yes. This is a key aspect of their design. The system integrator is responsible for providing the bearings to support the rotor and an encoder to provide position feedback. This allows for complete design flexibility.
Q3: How difficult is it to integrate a frameless torque motor into a custom housing? While it requires careful mechanical design and precision machining of the housing, the integration process is straightforward for experienced engineers. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for alignment and air gap is crucial. For assistance, you can always .
Q4: Can a direct drive motor be used in high-speed applications?